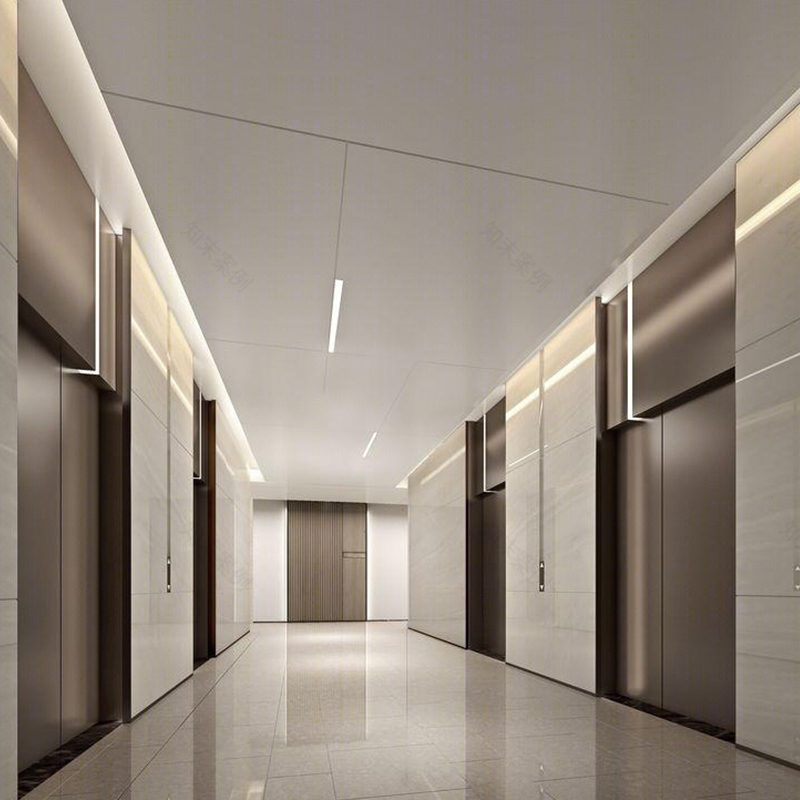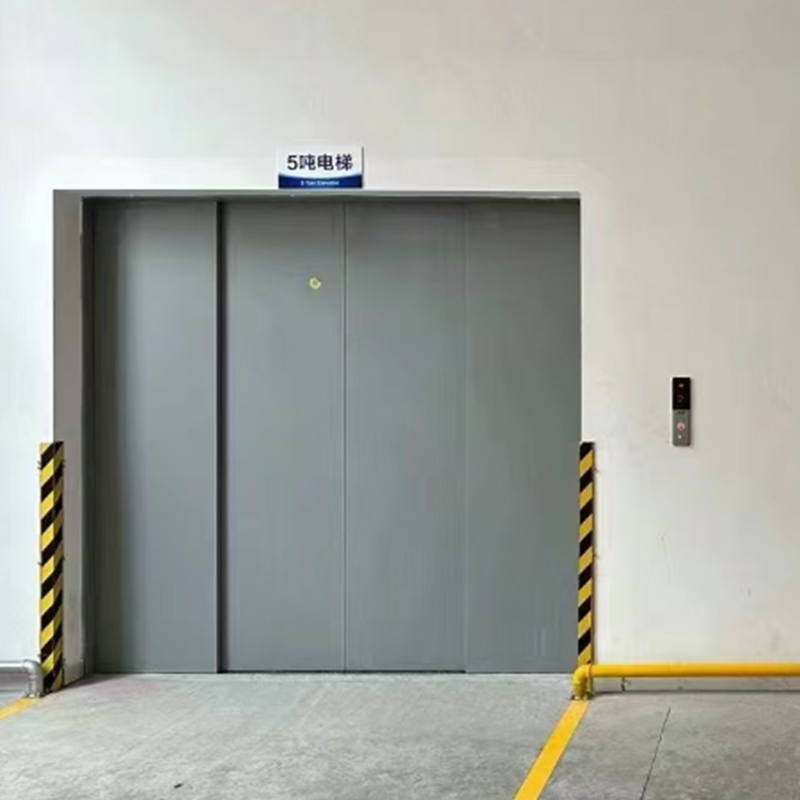
Why Should You Consider a Trailing Platform Ladder for Your Worksite?
Posted by Admin | 25 Nov
Choosing a Trailing Platform Ladder Over a Conventional Ladder
When you are managing an outdoor event, theater setup, or any worksite that requires frequent access to elevated areas, a trailing platform ladder often presents advantages that a conventional ladder cannot match. A traditional ladder must lean against or rest against a structure, relying heavily on a stable wall or support and presenting limitations in mobility and reach. In contrast, a trailing platform ladder integrates a walking platform and trailing mechanism that allows you to traverse along a path or track while maintaining elevation. This means workers can move laterally at height rather than climbing up and down repeatedly, reducing fatigue and improving efficiency. The stability is enhanced because the trailing system can anchor or roll on tracks, distributing weight more evenly. In many outdoor environments where terrain is uneven or support structures are distant, the trailing platform ladder offers a more flexible, safer, and more effective solution.
Design Considerations Across Different Scenarios
Not every work environment has identical demands, so the design of a trailing platform ladder must adapt to different scenarios. For outdoor theater or stage installations, the ladder must span significant horizontal distances, sometimes crossing open space between scaffolding or stage edges. That demands careful calculation of span, support points, and allowable deflection. In agricultural settings, such as orchards or vineyards, the ladder may need to follow rows of trees or tracks, so lateral mobility and compatibility with ground conditions become critical. The ladder must be resilient to environmental factors like humidity, rain, or sunshine; thus, material choice and protective coatings are vital. Indoor use may require narrower widths, quieter travel, or nonmarking wheels or surfaces to avoid damaging flooring. Hence, designers must account for load capacity, corrosion resistance, width clearance, and interface with ground surfaces, tailoring the trailing platform ladder to the intended scenario.
Adjustability, Safety Features, and Installation Best Practices
To make a trailing platform ladder truly practical, adjustability and safety are nonnegotiable. A height-adjustable frame with locking mechanisms ensures that the working platform can reach multiple elevations securely, accommodating varied tasks. Safety features such as guardrails, toe boards, wide non-slip treads, and mid-rail supports prevent falls and ensure worker confidence. When installing the ladder setup, attention must be paid to anchor points, base stability, and ensuring that the trailing path is level or has controlled gradients. The interface between the ladder legs and the ground must prevent sinking or sliding, using properly designed footings or base plates. The alignment of trailing wheels or sliding rollers must be precise to avoid binding. It is critical to verify that all bolts, pins, and locking elements are properly tightened and secured before use, and that the platform is rigid and does not sway under load.
Material, Weight, and Mobility Trade-offs
Material selection plays a pivotal role in how practical the ladder will be in daily use. Aluminum alloys are lightweight and resist corrosion, making them ideal for portable systems in outdoor use, though they can cost more and may flex more under load. Steel is stronger and more economical but heavier and more susceptible to rust, thus requiring protective finishing. Composite materials can provide a balance of weight and durability, though their structural behavior must be well understood. In terms of mobility, wheels or casters can enable repositioning of the ladder, but such mechanisms must lock securely to prevent drift during use. A design that enables folding, telescoping sections, or modular dismantling can help with transport and storage. The challenge lies in balancing a low weight for ease of movement with sufficient structural strength and rigidity when deployed, ensuring that the ladder remains stable even as workers walk or carry loads on the platform.
Usage and Maintenance Advice
Once you have deployed a trailing platform ladder, regular maintenance and careful usage will preserve safety and prolong lifespan. In outdoor conditions, washing off dust, debris, salt deposits, or mud regularly helps prevent abrasion and corrosion. Inspecting welds, joints, sliding parts, rollers, and locking pins for wear or deformation ensures early detection of issues. Lubricate moving parts in controlled amounts (avoiding overgreasing) to maintain smooth operation. If the ladder is exposed to harsh weather, consider covering or storing it in a sheltered location when not in use. During use, instruct operators always to check stability, ground contact, and that guardrails and supports are locked. Avoid overloading, sudden movements, or lateral pushes that exceed design intent. In windy conditions, extra caution is necessary. Periodic load testing or certification checks help confirm structural integrity. By adhering to a disciplined maintenance schedule and safe operating norms, a trailing platform ladder can serve reliably for years, providing a safer and more efficient alternative to conventional ladders in challenging work environments.

-
 Founding Road, Qidu Linhu Economic Zone, Wujiang City, Jiangsu Province, China
Founding Road, Qidu Linhu Economic Zone, Wujiang City, Jiangsu Province, China
-
 [email protected]
[email protected]
-
 +86 17701557926/+86 0512-63818375
+86 17701557926/+86 0512-63818375


 En
En English
English русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى





